
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Itaru Hasegawa, Takuya Koizumi, Kazuhiko Kita, Masanori Suzuki, Toshih ...Article type: Regular Article
2021 Volume 85 Issue 7 Pages 247-255
Published: July 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 25, 2021
Advance online publication: June 04, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA new method of designing a flux for the copper alloy melting process that can achieve a good balance between the suppression of refractory corrosion by the flux and the acceleration of MnO dissolution into the flux was proposed. In this study, NN (neural network) computation was used to evaluate the refractory corrosion by the flux, and the predicted amounts of corrosion of refractories were in good agreement with experimental data. For the evaluation of the properties related to the MnO dissolution into the flux, both the viscosity of fluxes and the activity of MnO in fluxes were examined using thermodynamic analysis. By integrating the results of the above evaluations, an efficient method of designing the flux composition was devised. As an example of the application for this method, SiO2-55 mass% Na2O flux was found to be the optimal flux when Al2O3 refractory was employed.
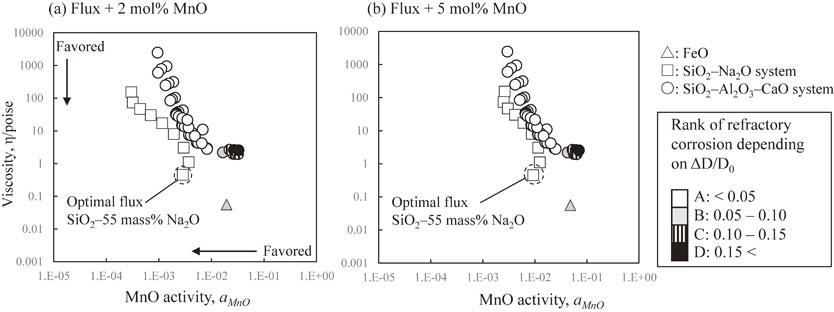 View full abstractDownload PDF (3318K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3318K) Full view HTML -
Nana Hashimoto, Ken-ichi Ikeda, Seiji Miura, Koji Morita, Tohru S. Suz ...Article type: Regular Article
2021 Volume 85 Issue 7 Pages 256-263
Published: July 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 25, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTo clarify the effect of constraint conditions on the kink formation, fabrication process of the texture and porosity controlled Ti3SiC2 polycrystals was investigated and microstructural evolution during high temperature deformation was examined in it under high temperature uniaxial compression tests at 1200℃. Dense textured Ti3SiC2 sintered body was fabricated by slip casting in the high magnetic field of 12 T and following pressureless sintering at 1400℃ for 1 h. The porosity of the textured Ti3SiC2 was controlled by dispersing polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) particles into the textured Ti3SiC2 as a spacer media. The highly textured Ti3SiC2 polycrystals with porosity of 8.4 vol% and 16.7 vol%, respectively, were successfully fabricated by the slip casting in the high magnetic field. After the high temperature uniaxial compression perpendicular to the c-axis of the textured structure, both the porous and dense Ti3SiC2 showed kink formation, which is a common deformation mode for anisotropic layered materials. However, the average rotation angles of the kink boundaries were higher in the porous specimen than in the dense specimen. Since the crystal rotation is necessary for the kink formation, kink bands would be preferably developed in the porous area due to its weaker constraint than in the dense area. It can be concluded from the microstructural analysis that the constrain factor caused by the neighbor grains affects the crystalline rotation, resulting in the kink boundary formation with different rotation angles.
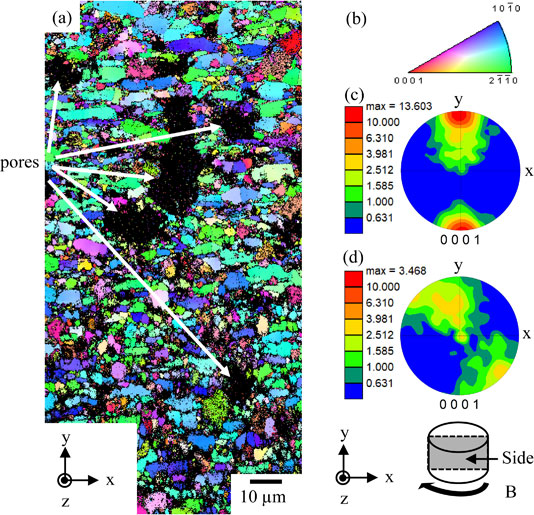 Fig. 5 (a) IPF map of the sintered body and (b) its color-coded map. (c) PF of (0001) plane of (a), and (d) PF of (0001) plane of non-textured sintered body for comparison. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (6420K) Full view HTML
Fig. 5 (a) IPF map of the sintered body and (b) its color-coded map. (c) PF of (0001) plane of (a), and (d) PF of (0001) plane of non-textured sintered body for comparison. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (6420K) Full view HTML -
Kentaro Ochi, Makoto Sekiguchi, Satoshi Oue, Hiroaki NakanoArticle type: Regular Article
2021 Volume 85 Issue 7 Pages 264-272
Published: July 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 25, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTo investigate the effect of polymer additives and chloride ions on the electrodeposition behavior and morphology of copper powder, the polarization curves were measured and constant current electrolysis of 300 A·m−2 and 500 A·m−2 was conducted in an electrolytic solution containing 0.079 mol·dm−3 of Cu2+ and 0.5 mol·dm−3 of free H2SO4 at 293K and 393 K without stirring. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polyethyleneimine (PEI) were used as polymer additives. PEG and PEI had a suppressing effect on the electrodeposition of copper powder. The current efficiency for Cu deposition decreased with the addition of PEG and PEI. The addition of PEG decreased the average particle size of the copper powder, while PEI didn’t change the average particle size. When Cl− coexisted with PEG, the suppressing effect on the electrodeposition of copper powder became even greater and the particle size of the copper powder became finer than when Cl− or PEG was added alone.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (7019K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (7019K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|