
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Daiki Harada, Yoshihiro TeradaArticle type: Regular Article
2022 Volume 86 Issue 12 Pages 233-236
Published: December 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2022
Advance online publication: October 21, 2022JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe age-hardening behavior of the Fe-Ni-based alloy HR6W without carbon was investigated at temperatures between 973 and 1173 K for a maximum of 3000 h to clearly identify the nose temperature of the Fe2W Laves phase. The microstructure observation was carried out for the aged alloys using field-emission scanning electron microscopy. One-step increase of hardness was detected for the alloy, which corresponds to the precipitation of Fe2W phase. It was found that the Fe2W phase precipitates with a flake-like morphology within γ grain interior and with a granular morphology at grain boundaries. The TTP (time-temperature-precipitation) diagram for the alloy is established based on the results of hardness measurements and microstructure observations, and the C curve representing the time required to initiate precipitation of the Fe2W Laves phase within γ grain interior was determined. The nose temperature of the C curve was identified as 1100 K, and the precipitation starts at 20 h at the nose temperature. The precipitation of the Fe2W phase at grain boundaries occurs for one order of magnitude earlier than that within γ grain interior at temperatures below 1100 K.
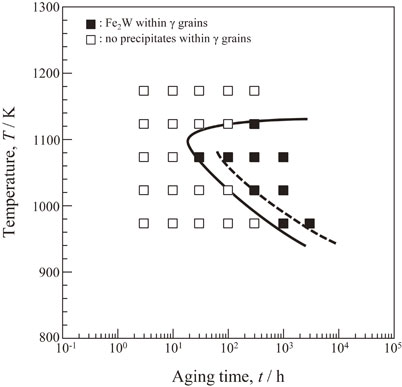 Fig. 3 TTP (time-temperature-precipitation) diagram of the HR6W without carbon within the γ grain interior. The C curve of the Fe2W Laves phase for the conventional HR6W obtained in the previous paper is included (dashed line)10). Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2605K) Full view HTML
Fig. 3 TTP (time-temperature-precipitation) diagram of the HR6W without carbon within the γ grain interior. The C curve of the Fe2W Laves phase for the conventional HR6W obtained in the previous paper is included (dashed line)10). Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2605K) Full view HTML -
Yasutoshi Hideshima, Fumiya Maeda, Tadao Fukuta, Koichi OzakiArticle type: Regular Article
2022 Volume 86 Issue 12 Pages 237-244
Published: December 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2022
Advance online publication: October 28, 2022JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMagnesium chips were coated with a high concentration of graphite using a binder, and then used as the raw material for thixomolding. The microstructure of the magnesium injection-molded product with the addition of graphite exhibited a dispersion of needle-like graphite. No significant voids were observed at interfaces between the graphite and matrix. The addition of more than 0.5 mass% graphite decreased the proof stress and tensile strength of the injection-molded products. The Young’s modulus of graphite-added products showed a tendency to decrease with increasing addition of graphite, which was consistent with the lower limit of the rule of composites. Compared to AZ91D, the thermal conductivity of the 6.9 mass% graphite-added product was increased, and the coefficient of linear thermal expansion was decreased. Both were within the ranges where the rules of mixtures were satisfied.
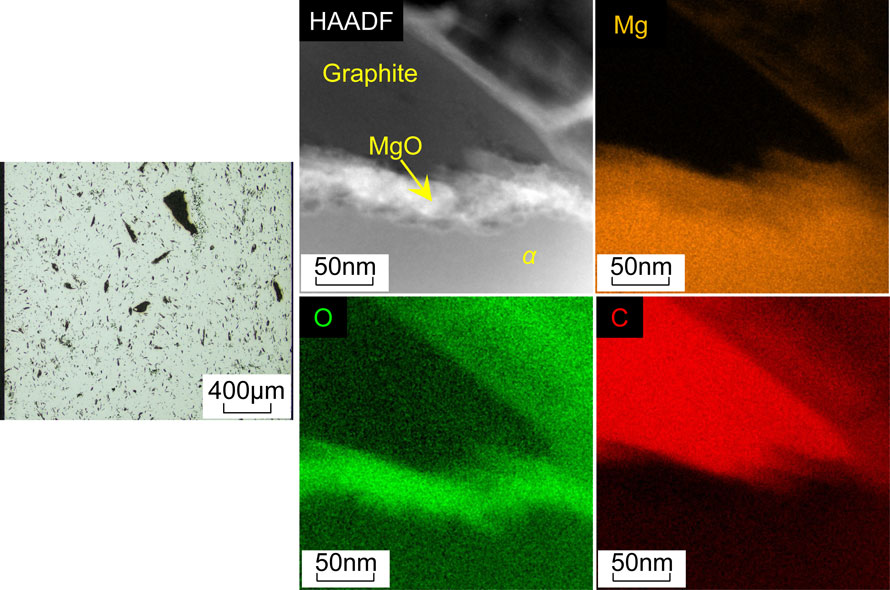 Microstructure of graphite-dispersed magnesium matrix composites and interface between matrix and graphite Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4779K) Full view HTML
Microstructure of graphite-dispersed magnesium matrix composites and interface between matrix and graphite Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4779K) Full view HTML -
Jun Yaokawa, Keiichiro Oh-ishi, Shuxin DongArticle type: Regular Article
2022 Volume 86 Issue 12 Pages 245-251
Published: December 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2022
Advance online publication: October 28, 2022JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAl-10Si-Mg alloy have been used for die casting and additive manufacturing. In this study, solution-treated Al-10Si-Mg and Al-10Si alloys (mass%) were heat-treated at several temperatures and the linear dimensional changes arising from the heat-treatments were investigated. A theoretical model for calculating the linear dimensional change in Al-Si-Mg ternary alloys was proposed, and the theoretically and the experimentally determined linear dimensional changes were compared. It was found that the linear dimensional changes of Al-10Si-Mg and Al-10Si alloys were almost the same. In both alloys, the linear dimensional changes increased with the decrease of the heat-treatment temperature. The linear dimensional changes of Al-10Si-Mg and Al-10Si alloys agreed well with the values estimated by the proposed theoretical model.
Mater. Trans. 62 (2021) 1023-1029に掲載
 Fig. 9 Measured and calculated linear dimensional changes of solution-treated Al-10Si-Mg alloy specimens due to heat treatment. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2943K) Full view HTML
Fig. 9 Measured and calculated linear dimensional changes of solution-treated Al-10Si-Mg alloy specimens due to heat treatment. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2943K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|