
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Kaname Matsumoto, Hiroaki KumakuraArticle type: Regular Article
2019 Volume 83 Issue 9 Pages 293
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 25, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML -
Goro OsabeArticle type: Overview
2019 Volume 83 Issue 9 Pages 294-304
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 25, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAfter the over-pressure sintering method and the pre-tensioned lamination technique were introduced, critical current and mechanical properties of Ag-sheath Bi-2223 wire have been drastically improved, though further enhancement of their properties is necessary for promoting practical applications. This paper reviews the recent understanding of the critical current properties and improvement of the mechanical properties, and introduces achievements of Ag-sheath Bi-2223 wire which have been used for current lead, cable, magnet and motor applications.
 Fig. 7 EBSD and IPF results of the mass production Bi-2223 wire and developed high Jc Bi-2223 wire. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1276K) Full view HTML
Fig. 7 EBSD and IPF results of the mass production Bi-2223 wire and developed high Jc Bi-2223 wire. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1276K) Full view HTML -
New Microstructure Control for Internal Tin Processed Nb3Sn Wires through Element Addition to MatrixNobuya Banno, Taro Morita, Zhou Yu, Tsuyoshi Yagai, Kyoji TachikawaArticle type: Review
2019 Volume 83 Issue 9 Pages 305-313
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 25, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLFurther performance improvement in Nb3Sn conductors is strongly demanded towards realization of upcoming high-field magnet applications such as the Future Circular Collider (FCC) and the DEMOnstration power plant (DEMO). However, we are facing the problem that the Jc performance of the Nb3Sn strands are almost fully optimized in terms of Nb/Cu/Sn area ratio, cross-sectional design, Nb filament diameter, and so on. We thus need some breakthrough to overcome the problem. In this context, we have been studying the new microstructure control by the element addition into the Cu matrix of the internal tin processed Nb3Sn conductors. In this paper, some results of the more fundamental study on the effect of the Zn addition are reported. In addition, results of the simultaneous addition of Zn and a small amount of Mg, and the influence of Ti-doping position on the microstructure and Jc performance are reported. It was found that significantly different diffusion behaviors happen in the Cu-Zn/Sn diffusion reaction. For instance, in the Cu-Zn/Sn diffusion, a solid ternary Cu-Sn-Zn phase widely forms at the outermost reaction front at 400℃ heat treatment, whereas the porous ε phase widely forms in the Cu/Sn diffusion. A small addition of Mg into the brass matrix resulted in finer grain size and better Jc performance. Ti doping to the Nb filaments but not Sn cores leads to elimination of Ti-rich layer at the boundary that forms in Ti doping to Sn cores. The absence of Ti-rich layer contributes significantly to improvement of Sn and Ti distribution across the cross-section.
 Fig. 1 BSE images of reaction layer of (a) Cu/Sn-1.6 mass%Ti and (b) brass (Cu-12 mass%Zn)/Sn-1.6 mass%Ti diffusion couples after heat treatment at 50 h/210℃, 30 h/400℃ and 10 h/550℃28). Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3632K) Full view HTML
Fig. 1 BSE images of reaction layer of (a) Cu/Sn-1.6 mass%Ti and (b) brass (Cu-12 mass%Zn)/Sn-1.6 mass%Ti diffusion couples after heat treatment at 50 h/210℃, 30 h/400℃ and 10 h/550℃28). Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3632K) Full view HTML -
Kazuki Sugihara, Yusuke Ichino, Yuji Tsuchiya, Ataru Ichinose, Yutaka ...Article type: Regular Article
2019 Volume 83 Issue 9 Pages 314-319
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 25, 2019
Advance online publication: February 18, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn the longitudinal magnetic field state, critical current density (Jc) of a superconductor enhances compared with the Jc in self-field and it is called as Jc gain. We have reported Jc gain in BaHfO3-doped-multilayered (ML) SmBa2Cu3Oy(Sm123) films on oxide single crystalline substrates. In this study, we aim for the Jc gain appearance in ML-Sm123 films on IBAD-MgO metal tapes for power cable application. We observed the Jc gain on metal tapes with good reproducibility. From viewpoints of the flux pinning and super-current flow, important factors for the Jc gain at 77 K were higher interface density, self-organized BHO nanorods with larger diameter, and the reduction of a ML-structure disturbances.
 Fig. 1 Normalized Jc-B curves of Sm123 films at 77 K in B//ab,B//I (longitudinal magnetic field state). Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1474K) Full view HTML
Fig. 1 Normalized Jc-B curves of Sm123 films at 77 K in B//ab,B//I (longitudinal magnetic field state). Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1474K) Full view HTML -
Tomoya Horide, Kenta Torigoe, Ryusuke Kita, Ryota Nakamura, Manabu Ish ...Article type: Regular Article
2019 Volume 83 Issue 9 Pages 320-326
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 25, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLImprovement of critical current density (Jc) in magnetic fields is required in YBa2Cu3O7 films, and process parameters should be optimized for controlling pinning centers. In the present study, a deposition temperature was varied in pulsed laser deposition of YBa2Cu3O7+BaHfO3 films to control the nanorod structure, and its influence on Jc was analyzed. The YBa2Cu3O7+BaHfO3 film deposited at 850℃ exhibited pinning force maximum (Fp,max) as high as 413 GN/m3 at 40 K, while the Fp,max for the deposition temperature of 850℃ at 77 K was smaller than that in the YBa2Cu3O7+BaHfO3 film deposited at 900℃. A critical temperature decreased and matching field increased with decreasing the deposition temperature. Increase in deposition temperature is effective in improving the Fp,max in high temperatures, since the critical temperature and matching field dependences of Jc value dominate the Fp,max. On the other hand, low deposition temperature improves the Fp,max in low temperatures since the Fp shift in accordance with matching field is dominant to the Fp,max. Thus, the deposition temperature should be set in pulsed laser deposition of YBa2Cu3O7 films containing nanorods considering the Jc variation with critical temperature and matching field.
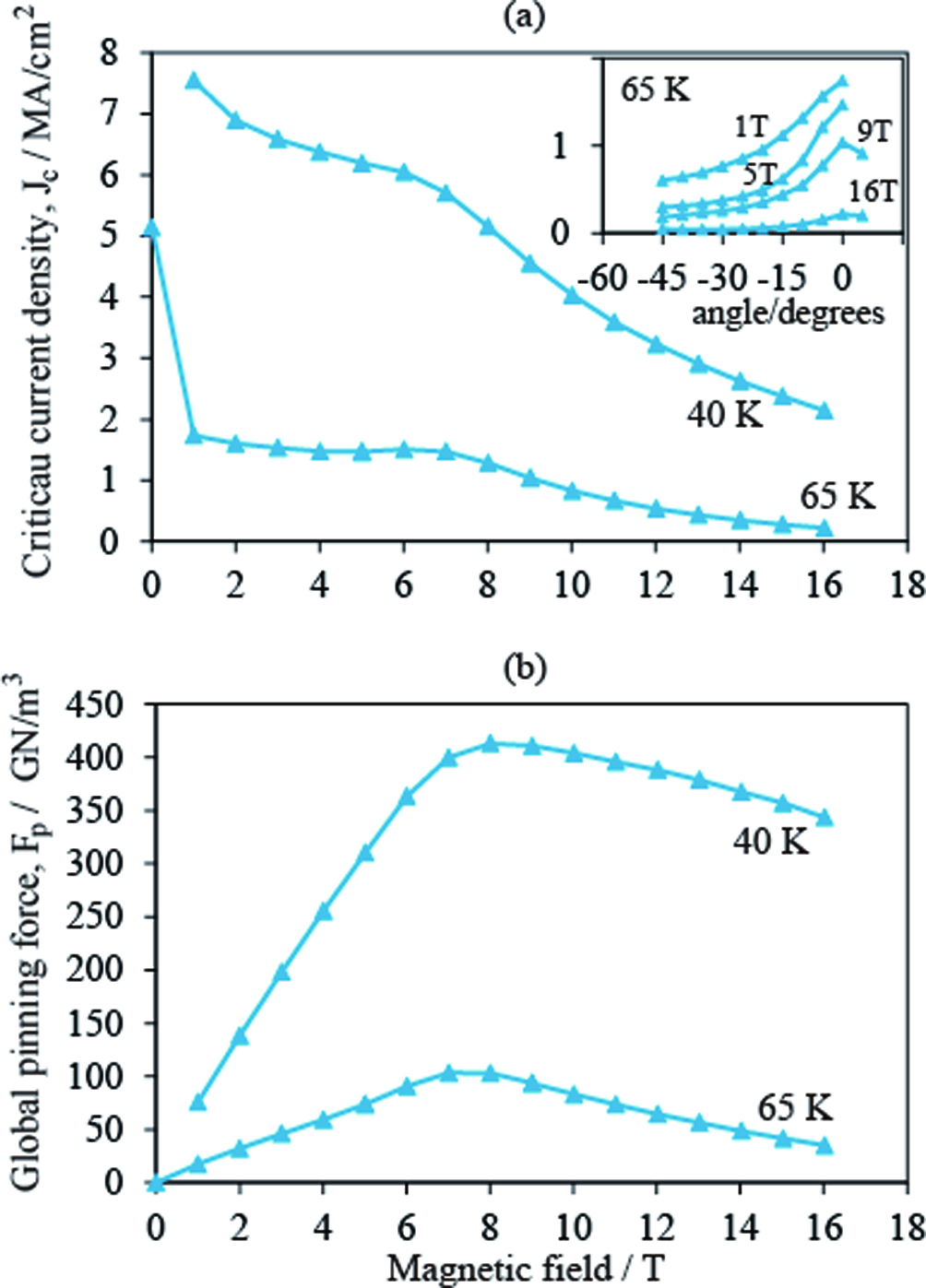 Fig. 3 Magnetic field dependences of (a) Jc and (b) Fp in temperatures of 40 K and 65 K for the YBCO+BHO(850) film. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1196K) Full view HTML
Fig. 3 Magnetic field dependences of (a) Jc and (b) Fp in temperatures of 40 K and 65 K for the YBCO+BHO(850) film. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1196K) Full view HTML -
Ataru Ichinose, Kiyosumi Tsuchiya, Akihiro Kikuchi, Hidetoshi OguroArticle type: Regular Article
2019 Volume 83 Issue 9 Pages 327-334
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 25, 2019
Advance online publication: May 31, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTo adopt coated conductors to various superconducting devices, characteristics such as microstructure and critical current of commercially available coated conductors were investigated. The microstructure was analyzed using a transmission microscope with an energy dispersion spectroscopy. The critical current (IC) were measured at 4.2 K and magnetic fields (B//c), and at 77 K and self-magnetic field. As a result of microstructure analyses, the magnetic field dependencies on IC at 4.2 K are found to depend on the microstructure of the superconducting layer. Moreover, almost coated conductors were found to have a potential to improve their IC at 77 K and self-magnetic field.
 Fig. 1 Cross-sectional STEM images of (a) AMSC, (b) Fujikura, (c) Shanghai SC, (d) Sumitomo, (e) SuNAM, (f) SuperOX, (g) SuperPower1 and (h) SuperPower2. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (7790K) Full view HTML
Fig. 1 Cross-sectional STEM images of (a) AMSC, (b) Fujikura, (c) Shanghai SC, (d) Sumitomo, (e) SuNAM, (f) SuperOX, (g) SuperPower1 and (h) SuperPower2. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (7790K) Full view HTML -
Yuji Tsuchiya, Shuya Tajiri, Yusuke Ichino, Ataru Ichinose, Yutaka Yos ...Article type: Regular Article
2019 Volume 83 Issue 9 Pages 335-340
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 25, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLHigh-temperature superconducting REBa2Cu3Oy (RE: Rare earth elements, REBCO) films need both a high-speed film fabrication with a well-oriented crystalline texture and an introduction of artificial pinning centers (APCs) to improve critical current densities Jcs in magnetic fields.A vapor-liquid-solid (VLS) growth method enables the REBCO films to grow rapidly with a high quality but makes it difficult to introduce the APCs.In this study, Y2BaCuO5 (Y211) was doped into YBa2Cu3Oy (Y123) films fabricated via the VLS method with a liquid layer of Ba3Cu7O10.A microstructure analysis revealed that nano-particle APCs with diameter less than 10 nm were successfully introduced into the YBCO films.The Y211-doped Y123 films show the highest critical temperature Tc and the Jc in magnetic fields with a chemical composition ratio close to the stoichiometry of Y123.
 Fig. 1 Schematic drawing of (a) VLS growth method and (b) surface modified target for Y211-doped VLS-Y123 films. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1353K) Full view HTML
Fig. 1 Schematic drawing of (a) VLS growth method and (b) surface modified target for Y211-doped VLS-Y123 films. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1353K) Full view HTML -
Yu Sanogawa, Akiyasu YamamotoArticle type: Regular Article
2019 Volume 83 Issue 9 Pages 341-345
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 25, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMagnesium Vapor Transport method (MVT method) has been developed, in which magnesium vapor is treated with boron to obtain MgB2 superconducting polycrystalline bulks. The obtained disk-shaped MgB2 bulk with 20 mm in diameter and 2 mm in thickness had high packing factor of 80% and high phase purity. The critical current density Jc reached 800000 A/cm2 at 20 K under self-field, which is about twice as high as a sample produced by the conventional in situ technique, due to the reduction of voids and impurities. Trapped field of 1 T was measured at 10 K at the surfaces of the thin disk-shaped bulk. Our results show that MVT method is one of the most effective techniques to extract superior trapped field performance of polycrystalline bulk MgB2 magnets through enhancing circulating supercurrent density and bulk size both of which are essential for high field trapped field magnets.
 Fig. 2 Appearance photograph of MgB2 bulk produced by the MVT process. The central part is bulk MgB2 (diameter 20 mm, thickness 2 mm). The outer part is a reinforced steel ring. Hexagonal structures developed around circles corresponding to the Mg diffusion holes can be observed. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (7329K) Full view HTML
Fig. 2 Appearance photograph of MgB2 bulk produced by the MVT process. The central part is bulk MgB2 (diameter 20 mm, thickness 2 mm). The outer part is a reinforced steel ring. Hexagonal structures developed around circles corresponding to the Mg diffusion holes can be observed. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (7329K) Full view HTML -
K. Togano, Z. Gao, A. Matsumoto, A. Kikuchi, H. KumakuraArticle type: Regular Article
2019 Volume 83 Issue 9 Pages 346-351
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 25, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe fabrication of Fe-based Ba-122 superconducting tapes was studied by ex-situ powder-in tube (PIT) process using double sheathing technique of stainless steel (SS) and Ag-Sn alloy. We found that the double sheathed SS/Ag-Sn/Ba-122 tapes show much more improved critical current density (Jc) compared to the previously reported single sheathed Ag/Ba-122 tapes. By optimizing the Sn content, heat treatment temperature, and tape thickness, we have achieved high Jc of well over 105 A/cm2 at 4.2 K and 10 T, which is the target value for practical application. Taking into account coil winding in the future, we fabricated a ~1 m long SS/Ag-Sn/Ba-122 tape and evaluated the uniformity of Jc along tape length and the Jc degradation by bending. The Jc distributed within 5.5-7.2 × 104 A/cm2 (4.2 K, 10 T) over the entire length and showed no degradation until 3 cm diameter bending.
 Fig. 6 Ic distribution of the 80 cm long SS/Ag-5 at%Sn double sheathed Ba-122 tape along the tape length. The tape was heat treated at 750℃ for 2 h. The inset photograph is the tape after the heat treatment. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1789K) Full view HTML
Fig. 6 Ic distribution of the 80 cm long SS/Ag-5 at%Sn double sheathed Ba-122 tape along the tape length. The tape was heat treated at 750℃ for 2 h. The inset photograph is the tape after the heat treatment. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1789K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|