All issues

Volume 80, Issue 4
Displaying 1-11 of 11 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Regular Article
-
Toshihiro Omori, Tatsuro Morita, Kohei Okada, Hideaki Maeda2016 Volume 80 Issue 4 Pages 225-230
Published: 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2016
Advance online publication: February 05, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis study was conducted to improve fretting fatigue strength of austenitic stainless steel JIS SUS316 by the hybrid surface treatment composed of plasma nitriding (hereafter, PN) and fine-particle bombarding (FPB). In the study, finite element analysis (FEA) was also performed to investigate local stress-strain response induced at the contact edges in fatigue specimens. Since the above hybrid surface treatment didn't affect the microstructure in the substrate, there was no influence on the mechanical properties. Fretting fatigue strength was markedly improved by the hybrid surface treatment, and its improvement percentage reached 50%. The results of FEA showed that “shakedown” occurred at the contact edges under applied cyclic stress so that local mean stress there became zero. The formed hardened layer had no effect to improve wear condition at the contact edges. Accordingly, it was suggested that the improvement of fretting fatigue strength resulted from the increase in crystallographic slip resistance by the formed hardened layer.
View full abstractDownload PDF (4317K) -
Michihisa Fukumoto, Hiroshi Sonobe, Motoi Hara, Hiroyuki Kaneko2016 Volume 80 Issue 4 Pages 231-239
Published: 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2016
Advance online publication: February 12, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe oxidation behavior of Zircaloy 4 in Ar-H2O and Ar-O2-H2O (saturated water vapor at 323 K) gas mixtures has been examined under several temperature conditions using hydrogen and oxygen sensors to investigate the dependence of oxygen concentration and temperature changes. The results are summarized as follows. The amount of consumed oxygen that contributed to the oxidation could be calculated from the change in the oxygen partial pressure measured by the oxygen sensor. Furthermore, the amount of hydrogen generated through steam oxidation could be calculated from the change in the hydrogen partial pressure measured by the hydrogen sensor, and the amount of consumed oxygen could be concomitantly calculated. The relative contributions of oxygen-consuming and steam oxidation could be calculated with respect to the oxidation of Zircaloy. The oxygen-consuming oxidation proved to precede in the oxidation reaction, and the oxidation by steam oxidation progressed after the oxygen contained in the original gas had been completely consumed. When conducting isothermal oxidation experiments at 1173 K, only the oxygen-consuming oxidation occurred in an atmosphere above 1% oxygen without the progression of steam oxidation. At 1523 K, steam oxidation was observed even in 5% oxygen, because oxygen was intensely consumed in the initial stage of the reaction. When conducting temperature-increased oxidation experiments, oxygen was completely consumed in an atmosphere with 1% oxygen at approximately 1358 K, above which steam oxidation progressed. When performing thermal cycling oxidation experiments, it was clearly demonstrated that the region in which only oxygen-consuming oxidation occurred and the region in which steam oxidation added to the oxygen-consuming process on varying the temperature. As the cycling frequency was increased, the total amount of oxidation decreased and the contribution from the steam oxidation also decreased. The thermodynamics of the processes of oxygen-consuming and steam oxidation has been discussed.
View full abstractDownload PDF (5913K) -
Chitoshi Masuda, Mitsunori Kawaguchi, Masaki Yosioka, Fumio Ogawa, Hid ...2016 Volume 80 Issue 4 Pages 240-246
Published: 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAl-coated carbon nanofiber(CNF) reinforced aluminum matrix composites were fabricated by pressureless infiltration at 850℃ in the presence of N2 into a CNF-Mg-Al preform. Aluminum coating on the CNF was obtained by Chemical Vapor Deposition(CVD) in order to improve the wettability and aluminum coating layer was about 10 nm on the CNF surface at 500℃ and for holding time of 48 h. The effects of the preform fabrication conditions, such as pressure, temperature, and Mg contents on the infiltration were discussed. As the pressure was a 200 kPa at room temperature, the infiltration depth was largest. Moreover, Mg content was about 30% to obtain the largest infiltration depth. The ratio of non-coated to coated CNF was 0.5 to show the largest infiltration depth and the hardness and modulus of that composite including Al coated CNF were about Hv240 and 85 GPa, respectively.
View full abstractDownload PDF (2462K) -
Kana Umehara, Yasunari Matsuno2016 Volume 80 Issue 4 Pages 247-252
Published: 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPreviously we studied a novel process for recycling gold from secondary sources: the leaching of gold using dimethyl sulfoxide solutions containing copper bromide and precipitation with water, which could offer a number of advantages, including eco-friendliness, ease of operation and low cost. In this study, we have further investigated a more environmentally benign solvent, Propylene Carbonate (PC), with CuBr2 and KBr for the leaching and recovery of precious and rare metals. The mechanism of dissolution was investigated using electrochemical measurements. Metal wires were dissolved in a PC solution with 0.2 M of CuBr2 and 0.2 M of KBr at 343 K. Next, 10 ml of dilute sulfuric acid aqueous solution at pH 1 was added to the solution at ambient temperature and shaken to biphasically separate the dissolved metals. The contents of each element in the sulfuric acid and PC phases were measured by ICP-OES. The results of the electrochemical measurements indicated that the anodic dissolution of sample metals in the PC containing CuBr2 occurred at relatively negative potentials and was paired with the cathodic reduction of Cu2+ to Cu+. It was found that Au, Pd, Cu, Sn, Co, Ni and Zn could be dissolved at relatively fast rate, while Ag, Ta, Ti and W could not be dissolved. In addition, 98% of Au and 94% of Pd remained in the PC phase, while most other dissolved metals migrated to the sulfuric acid phase. This indicated that the dissolved Au and Pd could be effectively separated from other metals via biphasic separation with sulfuric acid. Next, the gold in the PC phase was recovered by the reduction of ascorbic acid or calcination. The cost analysis for recovering gold by this system resulted in 0.34 USD/g-Au.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1375K) -
Yasushi Hiraoka, Youichi Watanabe, Osamu Umezawa2016 Volume 80 Issue 4 Pages 253-258
Published: 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSLow alloy steels containing chromium, JIS-SCM435, DIN-31CrMoV9 and JIS-SACM645, were gas-nitrided at 773 K, 813 K and 853 K under several nitriding potentials, where the compound layer was generated at almost the beginning of the nitriding. Their hardness profiles and nitrogen distributions were characterized in the nitrogen diffusion layer. A linear relationship between the hardness increased, ΔHV, and nitrogen content in the diffusion layer was detected at each nitriding temperature in the steels. Their linear constants K were given by the Arrhenius type equation as a function of nitriding temperature in the steels. The hardness increased in the diffusion layer was demonstrated by the Orowan bypass mechanism for CrN platelets in DIN-31CrMoV9. The linear relationship in low alloy steels can be represented when the total volume fraction of precipitates such as CrN and AlN is less than several percent and their average particle size is less than 20 nm.
View full abstractDownload PDF (2759K) -
Yasushi Hiraoka, Youichi Watanabe, Osamu Umezawa2016 Volume 80 Issue 4 Pages 259-267
Published: 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA model to predict the diffusion layer's hardness profile in gas-nitrided low alloy steels such as JIS-SCM435, DIN-31CrMoV9 and JIS-SACM645 was successfully developed taking into account the following considerations. The diffusion of dissolved nitrogen in the surface boundary was given as the nitrogen flux, which can be determined by either the nitriding potential or thermo-equilibrium between α-Fe and γ′-nitride after the formation of the compound layer. The kinetics of CrN and AlN precipitations was characterized as the KP concerned with nucleation and diffusion of Cr or Al and the parabolic rate constant χ concerned with the growth of disc-shaped CrN and AlN. KH was defined as a proportional constant between the increase in hardness and the nitrogen concentration. KP and the solubility product KCrN for CrN were fitted well using the numerical model and the hardness profiles. KH was experimentally determined by using the hardness and nitrogen concentration in the diffusion layer. Then, the numerical results showed good agreement with the experimental ones. In SACM645especially, a more accurate calculation was demonstrated taking into account immobile excess nitrogen in the CrN and AlN.
View full abstractDownload PDF (3612K) -
Hiroki Kawamura, Katsuhisa Nagayama2016 Volume 80 Issue 4 Pages 268-272
Published: 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2016
Advance online publication: February 19, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe have previously reported the undercooling solidification behavior and high coercivity(Hc) of the Nd-Fe-based metastable phase using various containerless processes. However, the mechanism of high coercivity of the metastable phase is unclear. In this study, we have intended to examine the effect of Cu addition on the formation and high coercivity of Nd-Fe-based metastable phase using close to the stoichiometric composition of the Nd60Fe40 binary alloy. In addition, we have analyzed the relationship between high coercivity and the 3d-4f valence electron state by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis.
The Nd-Fe-Cu ternary particle samples were found to solidify by the drop tube process. The coercivity which was 5.8×103 Oe, increased by about two fold after Cu addition. X-ray diffraction (XRD) results showed that crystallization of the α-Nd phase was markedly suppressed in the Nd60Fe25Cu15 ternary particle samples. This is attributed to the increased production of the metastable phase by addition of Cu. The effectiveness of Cu addition on the formation of the metastable phase is suggested for this purpose. Using energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (EDS), the Nd-Fe-Cu ternary metastable phase composition ratio was found to be very similar to that of the Nd60Fe25Cu15 ternary based material (Nd:Fe:Cu=12:5:3).
From the XPS result for the Nd60Fe40 binary and Nd60Fe25Cu15 ternary particle samples, the 3d-4f bonding energy shifted to lower energy by Cu addition. Therefore, it is suggested that high coercivity depends on the increase of the 3d-4f electron bonding energy strength by the addition of Cu.
View full abstractDownload PDF (3337K) -
Yuya Takeda, Tadaharu Kawamura, Katsuhisa Nagayama2016 Volume 80 Issue 4 Pages 273-279
Published: 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2016
Advance online publication: February 05, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn general, quasicrystalline structures are produced by liquid quenching using a single roll, Bridgman and Czochralski method, which is typical for the production of single crystals. However, there are few reports of the quasicrystal formation using a containerless process; therefore, the effect of such a process is unclear.
In this study, we have investigated the production of quasicrystalline fine particles and the formation ability of Al63Cu25Fe12, Al65Cu20Fe15, and Al70Ni15Co15 ternary alloys using a drop tube apparatus with a free fall length of 2.5 m. In addition, we have aimed to examine the effectiveness of the drop tube process for quasicrystal formation.
The formation of dodecahedron crystals, which are considered a quasicrystalline phase, was observed in Al63Cu25Fe12 ternary fine particle samples prepared using the drop tube process under a He atmosphere (1 atm). Based on the heat flux, the calculated results suggested that the icosahedral phase was formed at high cooling rates of ~105 K/s. In the Al70Ni15Co15 ternary fine particle sample, aggregation of prismatic crystals was observed in the fine particle samples prepared using the drop tube process under an atmosphere of He (1 atm) and Ar (1 atm). Furthermore, formation of prismatic crystals was observed on the surface of fine particle samples prepared under a low-pressure Ar atmosphere (0.5 atm), under which the formation ability of quasicrystals was observed to be the highest. From these results, the formation ability of the Al-Ni-Co-based decagonal phase is suggested to increase with decreasing cooling rates. This result is different from that of the Al-Cu-Fe-based icosahedral quasicrystals.
View full abstractDownload PDF (4932K) -
Shumpei Miyata, Ryoichi Toyoda, Maki Hashimoto, Takaaki Iijima, Akira ...2016 Volume 80 Issue 4 Pages 280-283
Published: 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2016
Advance online publication: February 05, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn thin films that are prepared by sputtering, internal stress is generated during film formation. Internal stress is widely known to induce substantial changes in the properties of thin films, including their mechanical and optical properties and electromagnetic characteristics. The internal stress of sputtered films, which is generated by changes in their sputtering powers and gas pressures and substrate biases, is affected by ion bombardment during thin-film deposition. In our recent research, we studied methods of measuring the ion energy in the plasma and sheath regions using a multigrid electrostatic ion analyzer and a Langmuir probe. The obtained data suggested that the effect of ion bombardment can be quantitatively evaluated. In the present study, sputtered thin films were deposited using different sputtering gases and varying substrate biases. We attempted to control the internal stress of the deposited thin films by evaluating the ionic bombardment during film deposition as ion-bombardment parameter Pi, which was affected by the sputtering gas ions. The results demonstrate that the internal stress of the thin films decreased with increasing the ion-bombardment parameter Pi. The compressive stress was increased by the peening effect of the sputtering gas ions. Therefore, evaluating the internal stress of thin films using the ion-bombardment parameter Pi is feasible.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1056K) -
Narumi Suzuki, Ryosuke Sasaki, Yoshihito Matsumura, Masatoshi Kondo2016 Volume 80 Issue 4 Pages 284-288
Published: 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2016
Advance online publication: March 04, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESSOnline evaluation of the electrical properties of oxide layers was studied for the development of liquid breeder blanket of fusion reactors in this paper. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was applied for the layers of zirconium oxide formed at 773 K on the substrate of zirconium metal in air or pure oxygen gas atmospheres at the atmospheric pressure. The durations of the oxidation were 360, 900, and 1800 ks. The electrochemical impedance spectra for the oxidized surface of the Zr metals were measured at 773 K using the gold electrode fabricated on the sample surface by a sputtering method. The capacitance, the resistance, and the constant-phase-element parameter p (CPE-p) were evaluated from the measured spectrum of the samples by the comparison with the results of the model simulation for the layer using ZView code. Then, it was found that the thickness of the oxide layers estimated from the electrostatic capacitance was close to that from weight gain of the sample by its oxidation. It was indicated that the behavior of CPE-p depends on the atmospheres in the oxidation process. This result indicated that the composition and the structure of the oxide layers were not uniform and this behavior was influenced by the atmosphere for the oxidation procedure.
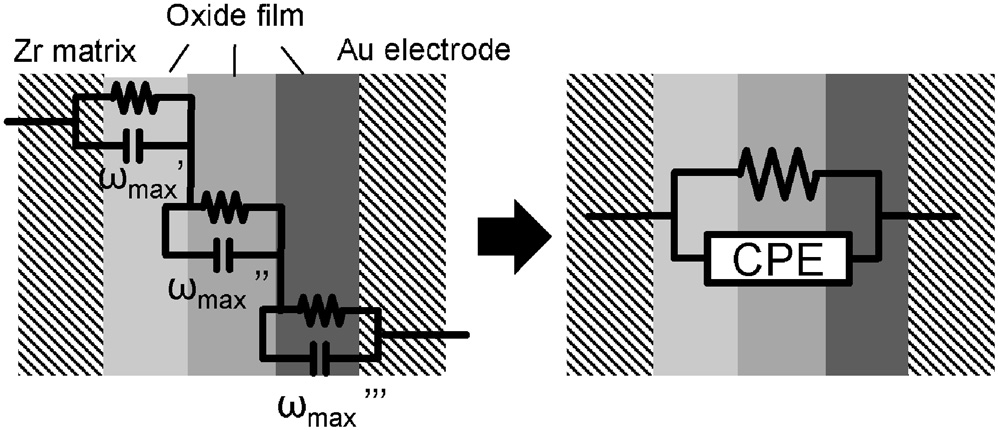 Fig. 13 Fullsize ImageSchematic representation of ununiformed oxide layer and equation circuit.View full abstractDownload PDF (3083K)
Fig. 13 Fullsize ImageSchematic representation of ununiformed oxide layer and equation circuit.View full abstractDownload PDF (3083K) -
Ayaka Takahashi, Keizo Hashimoto2016 Volume 80 Issue 4 Pages 289-296
Published: 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2016
Advance online publication: March 11, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSpacecraft which is used in harsh environments, may also encounter different problems on the ground. To prevent any problems, many of the sliding portions of a spacecraft are subjected to lubrication processing. WS2 solid lubricant coatings were fabricated by the heat treatment of a mixture of WS2 powder and an additive. To simulate deployment friction, experiments were conducted using a pin-on-disk of a tribometer at elevated temperatures in vacuum. The WS2 coatings were analyzed by Scanning electron microscope (SEM), Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) and Imaging plate x-ray diffraction (IPXRD) after friction tests. It was found that WS2 coatings showed a high performance with a friction coefficient of less than 0.1 at room temperature. This low friction coefficient was attributed to the reorientation of the (002) plane parallel to the disk surface. According to XRD analysis, the WS2 (002) plane has not been appered in a virgin disk. At high temperature, WS2 showed a low friction coefficient and it would had a sufficient lifetime up to 500℃. Although the initial friction coefficients were relatively high at elevated temperatures, friction coefficient at high temperature became the same as those at room temperatures. It can be rationalized that these WS2 coatings showed a high friction coefficient because additional force is necessary to reorientation of the stable WS2 aggregates.
View full abstractDownload PDF (4549K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|