
- Issue 4 Pages 185-
- Issue 3 Pages 113-
- Issue 2 Pages 47-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Hiromori Sagae, Masato Sugawara, Daiichiro Takahara, Michiaki Takagi, ...Article type: Regular Contribution
2025Volume 265Issue 4 Pages 185-191
Published: 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 11, 2025
Advance online publication: September 12, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLActivities of daily living (ADLs) with phantom limb pain (PLP) and prosthesis use in patients who underwent lower limb amputation for musculoskeletal malignancies has been reported just by a few researchers. This study aimed to investigate the influence of PLP and prosthesis use on ADLs after lower limb amputation for musculoskeletal malignancies. We conducted a retrospective study on 19 patients (10 males and 9 females) who underwent lower limb amputation for musculoskeletal malignancies between 2003 and 2011 and were followed up until 2021. The mean age was 60.4 (range, 10-85) years. We investigated PLP, prosthesis use, and ADLs after lower limb amputation; we used the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG-PS) to assess ADLs. PLP was present in 16 patients (84%), and 4 of 5 survivors (80%) were medication-free at the final follow-up. Prostheses were prescribed in 16 patients (84%), and 11 patients (69%) continued to use the prosthesis after discharge. In a multiple linear regression analysis of ADLs at discharge for the 15 patients with confirmed survival or death, excluding the four patients whose outcome was unknown at the last follow-up, lower-level amputation and good oncologic prognosis were positive independent factors, while age was the only negative independent factor. PLP and prosthesis use did not influence ADLs.
View full abstractDownload PDF (367K) Full view HTML -
Takuya Abe, Yumi Watanabe, Kaori Kitamura, Keiko Kabasawa, Toshiko Sai ...Article type: Regular Contribution
2025Volume 265Issue 4 Pages 193-200
Published: 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 11, 2025
Advance online publication: September 05, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialLow blood 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels at which C-reactive protein (CRP) levels begin to rise vary. This study investigated the association between blood 25(OH)D and elevated CRP levels and determine the cut-off of low 25(OH)D for elevated CRP in middle-aged and older individuals in the Murakami cohort, Japan. This study used a cross-sectional study design with 2,863 subjects aged 40-74 years living in the community. Plasma 25(OH)D levels were determined with the Liaison® 25OH Vitamin D Total Assay, and serum high sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) levels were determined with a latex nephelometry assay using an automatic analyzer. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to calculate odds ratios (ORs) for high hs-CRP (≥ 3 mg/L) with covariates including sex, age, BMI, physical activity, smoking, drinking, and disease history. Median age of subjects was 65 years, and median 25(OH)D level was 47.4 nmol/L. The proportion of subjects with high hs-CRP levels was 4.1%. The adjusted OR of 25(OH)D < 20 nmol/L was higher (OR = 3.22, 95% CI: 1.42-7.31) than that of the reference (25[OH]D 40-49 nmol/L). In subgroup analysis, the adjusted OR of 25(OH)D < 20 nmol/L was significantly higher than the reference in the BMI ≥ 22.8 (median) group (OR = 4.52) but not in the BMI < 22.8 group (OR = 1.61) (P for interaction = 0.0892), and the adjusted OR was significantly higher in the age ≥ 65 group (OR = 8.51) but not in the age < 65 group (OR = 2.22). Low blood 25(OH)D and high CRP levels were associated, with 25(OH)D 20 nmol/L being the cut-off, which was lower than previously reported values.
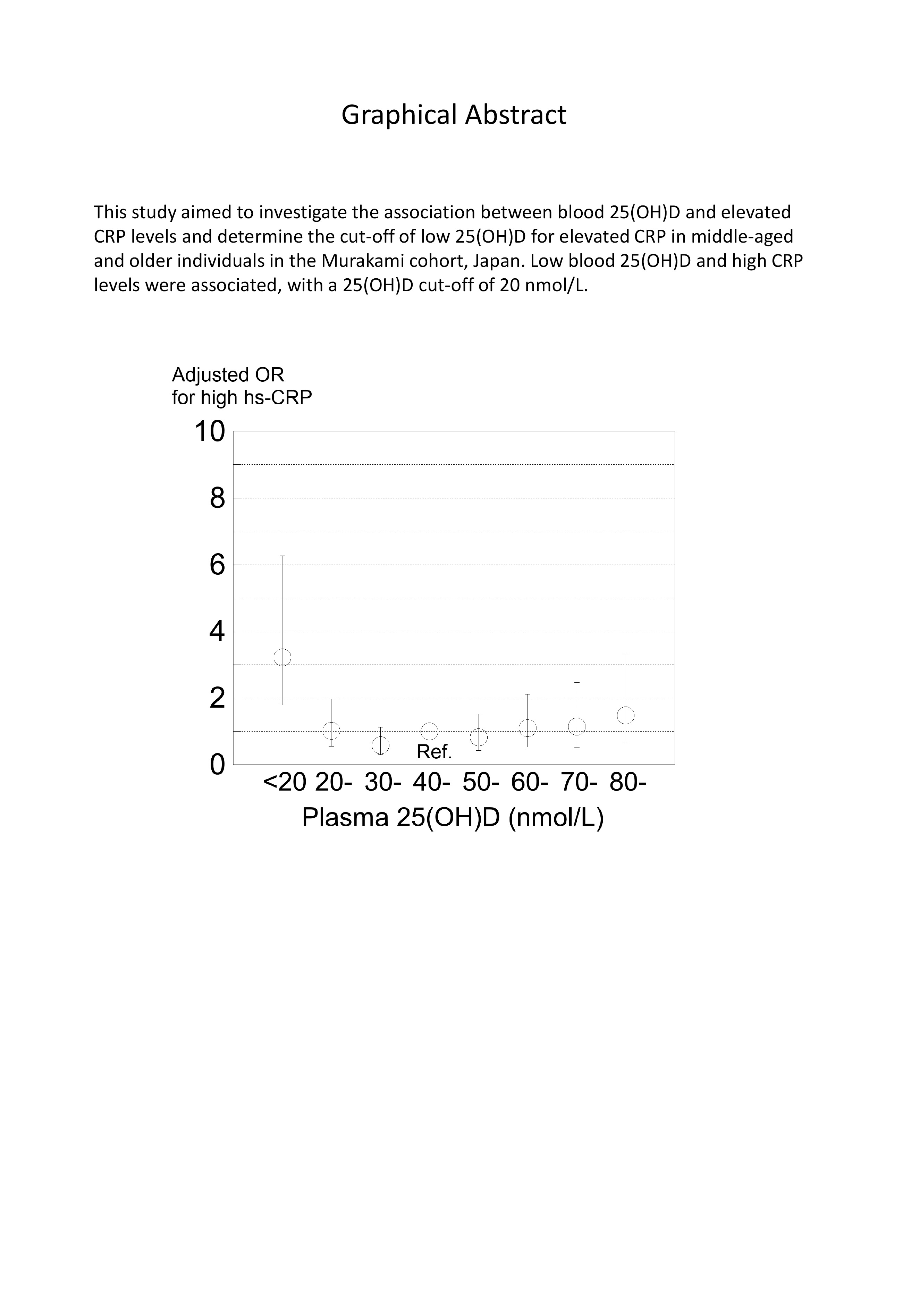 View full abstractDownload PDF (1249K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1249K) Full view HTML -
Yanqian Su, Huijuan Shi, Jue Tang, Siqi Zhao, Xuan Li, Jing Wang, Yanl ...Article type: Regular Contribution
2025Volume 265Issue 4 Pages 201-209
Published: 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 25, 2025
Advance online publication: September 12, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTriglyceride glucose (TyG) index has been discovered to be significantly associated with a higher risk of mortality. However, the specific association between the TyG index and all-cause mortality in psoriasis patients remains unclear. Data of this study came from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). The weighted multivariable Cox regression models and restricted cubic spline (RCS) models were applied to assess the association between the TyG index as continuous variables and tertiles and the risk of mortality. Kaplan-Meier (KM) methods were used to plot survival curves to describe the survival of participants. Additionally, sensitivity and subgroup analyses were conducted to test the robustness of the results. Psoriasis participants who died had substantially higher TyG index than those survived (9.00 ± 0.68 vs. 8.64 ± 0.60, P = 0.008). Multivariable Cox regression showed that TyG index was positively associated to the risk of all-cause mortality (hazard ratios (HR) 1.78, 95% confidence intervals (CI): 1.13-2.81; P = 0.012) after fully adjustment. After converting TyG index from a continuous variable to a categorical variable by tertiles, the unadjusted, partly-adjusted and fully adjusted HR for risk of all-cause mortality were 3.96 (95% CI: 1.47-10.7; P = 0.007), 3.10 (95% CI: 1.20-7.99; P = 0.019) and 3.05 (95% CI: 1.14-8.16; P = 0.027) in participants in tertile 3 of TyG index, compared with tertile 1. The significance of the association persisted across sensitivity and subgroup analysis. The TyG index was positively correlated with the risk of all-cause mortality among psoriasis. These findings suggest that TyG index may be a promising predictor of all-cause mortality for the psoriasis patients during the long-term follow-up.
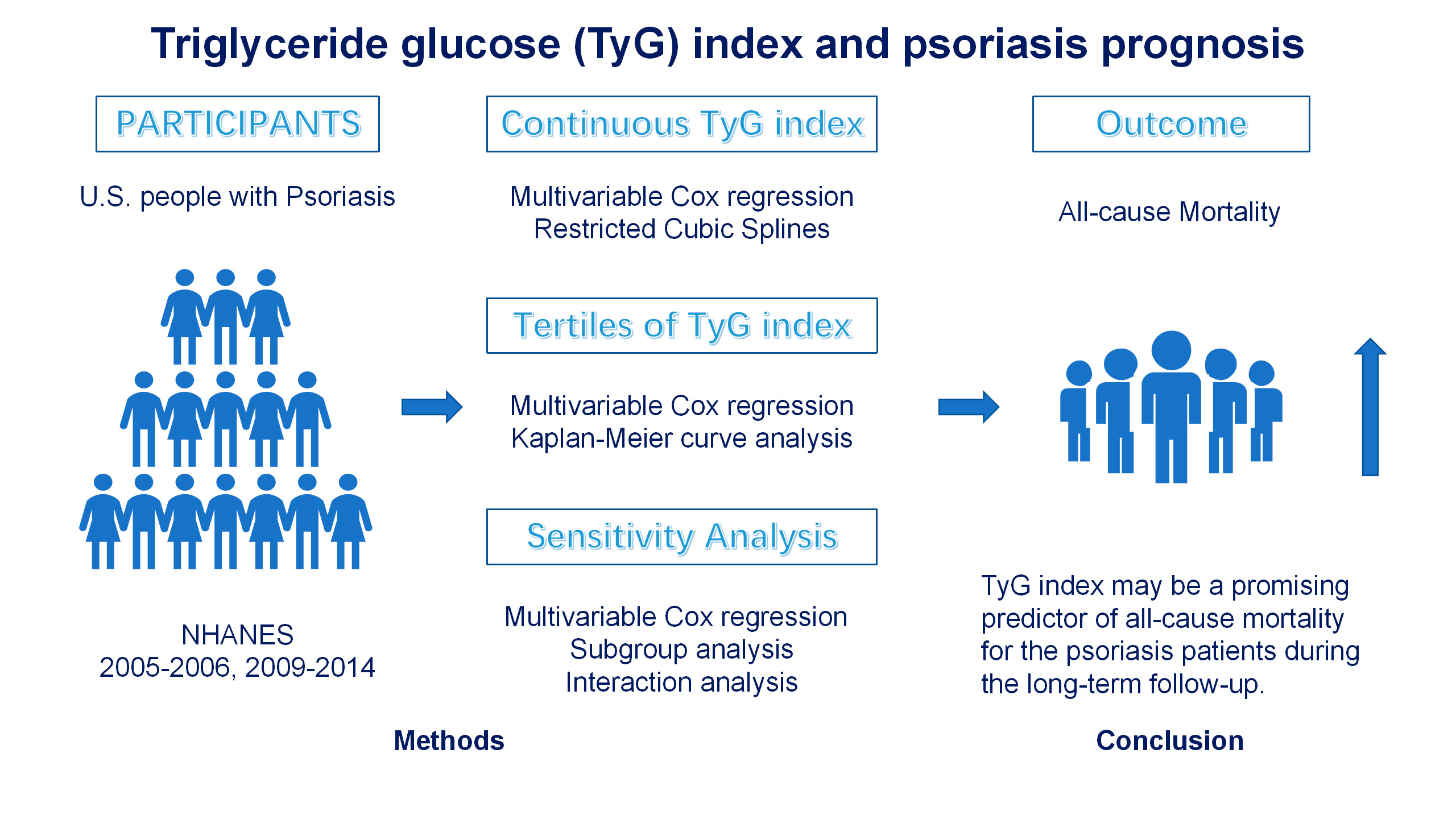 View full abstractDownload PDF (2389K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2389K) Full view HTML -
Hidetatsu Tanaka, Kunio Tarasawa, Yu Mori, Kiyohide Fushimi, Kenji Fuj ...Article type: Regular Contribution
2025Volume 265Issue 4 Pages 211-219
Published: 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 18, 2025
Advance online publication: September 12, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAn early surgery for older adult patients with hip fractures is recommended to avoid perioperative complications in existing clinical guidelines. Few studies have analyzed only transtrochanteric fractures. The purpose of this study was to assess whether surgery within two days of admission reduces the incidence of pneumonia, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, pressure ulcers, and mortality during hospitalization in patients with older adult transtrochanteric femur fractures. In this retrospective study, we used the Japanese National Administrative DPC (Diagnosis Procedure Combination) database that covers April 2016 to March 2022. Transtrochanteric femur fracture was included in patients aged 65 years or older who underwent surgery. The perioperative complications with pneumonia, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, pressure ulcers, and mortality during hospitalization were assessed after propensity score matching, focusing on surgeries conducted within two days of admission. After one-to-one propensity score matching for age, sex, and comorbidity, we identified 79,649 pairs of patients who underwent surgery either within two days or after the third day of admission. Surgery delayed beyond two days was independently associated with increased pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, pressure ulcers, and mortality during hospitalization with risk ratios of 1.335 (95% CI: 1.256-1.418, p < 0.0001), 1.287 (95% CI: 1.225-1.351, p < 0.0001), 1.229 (95% CI: 1.094-1.380, p < 0.0001), and 1.063 (95% CI: 0.978-1.155, p = 0.0035), respectively. Surgery within two days of admission for transtrochanteric femur fracture effectively prevents perioperative complications and reduces mortality during hospitalization.
View full abstractDownload PDF (420K) Full view HTML -
Zhicong Hong, Qiaoling Guo, Xianyang Luo, Liying LiuArticle type: Regular Contribution
2025Volume 265Issue 4 Pages 221-228
Published: 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 03, 2025
Advance online publication: September 12, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLNasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) has hidden onset, low rate of early diagnosis, and most of them have metastases at the time of diagnosis. The specific pathogenesis of NPC is still unclear. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are a large group of contaminants produced by the incomplete combustion of organic matter and widespread in the air. Many of these compounds are mutagenic and carcinogenic. PAHs plays an important role in mutagenic and carcinogenic, while its role in NPC still needs further elucidation. In this study, CNE-2 cells were stimulated by PAHs, then the expression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and CYP1A2 were respectively examined using Real-Time fluorescence quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western Blot. CNE-2 cells proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis were examined by CCK-8, Wound-Healing Assay, Transwell, Flow Cytometry, respectively. We found that AhR expression was increased while the level of apoptosis was inhibited by PAHs. While the ability of cell invasion was weakened, proliferation and migration were not significantly different. After treated by PAHs and ITE, the effect of PAHs on promoting AhR expression was significantly inhibited and apoptosis was up-regulated. The present study found that, PAHs inhibit apoptosis of NPC cells and promote the expression of AhR. Besides, PAHs participates in NPC occurrence and development by regulating AhR expression. Collectively, these findings may provide a possible strategy for the clinical treatment of NPC.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3511K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3511K) Full view HTML -
Kousuke Iba, Megumi Hanaka, Makoto Emori, Kenichi Takashima, Atsushi T ...Article type: Regular Contribution
2025Volume 265Issue 4 Pages 229-237
Published: 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 25, 2025
Advance online publication: November 07, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLBisphosphonate (BP) is mainly used for the treatment of osteoporosis because of its efficacy in increasing bone mineral density (BMD) and reducing osteoporotic fractures. Previous large-scale studies indicated that continuous 10-year treatment with BP was effective for osteoporosis treatment. However, several studies indicated an increase in the risk of serious adverse events such as atypical femoral fracture on prolonged BP treatment. The benefits and risks associated with long-term BP therapy are controversial. On the other hand, the effects of BP for more than 10 years are unknown because of few previous studies. The aim of this study to investigate effects of continuous 15-year treatment with BP on Japanese postmenopausal osteoporosis patients. The study was a retrospective observational study. Fifteen of the 55 patients, who had already received a 10-year course of oral BP treatment in our previous study, continued the treatment for an additional 5 years. All patients made the choice additional BP treatment with informed consent. BMD; hip structural analysis (HSA); limbs-muscle volume; and serum total alkaline phosphatase, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase-5b, calcium and phosphate levels were measured for 5 years in the 15 patients. BMD values at the lumbar spine were significantly increased at 15 years in comparison with that at 10 years. Section modulus of HSA for the intertrochanter was significantly increased at 15 years. No subsequent fractures or serious adverse events were observed. We demonstrated favorable effects of an additional 5 years of BP treatment in postmenopausal osteoporosis patients who had already received a continuous 10-year treatment.
View full abstractDownload PDF (415K) Full view HTML -
Yanwei Wang, Huifan Liu, Yali Feng, Shujuan Wu, Jingxuan He, Lei CaoArticle type: Regular Contribution
2025Volume 265Issue 4 Pages 239-248
Published: 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 26, 2025
Advance online publication: October 03, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLSepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI) has a high mortality rate, and cytokine storm is its feature. PANoptosis is a new type of cell death including apoptosis, pyroptosis and necroptosis. The aim of this study is to detect the PANoptosis level of lung macrophages, and to elucidate the new mechanism of sulforaphane (SFN) in sepsis-induced ALI. In septic animal model, the fluorescent staining of Caspase-8, GSDMD and p-MLKL and ASC/Caspase-8/RIPK3 PANoptosome in lung macrophages was performed. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used to induce macrophages to construct cell model of sepsis. The proportion of dead cells was detected by PI staining, and the expression of Bax, GSDMD-N, NLRP3 and p-MLKL was detected by western blotting. Search for the target genes of SFN and sepsis by network pharmacology. Molecular docking analysis confirmed the binding between SFN and TLR4. The protein levels of TLR4, P65 and p-P65 were detected by western blotting. The transcriptional levels of inflammatory factors were detected by qPCR. The expression of Caspase-8, GSDMD, p-MLKL and PANoptosome in septic lung macrophages was significantly increased, suggesting PANoptosis was up-regulated. LPS induced macrophages death and increased protein levels of Bax, GSDMD-N, NLRP3 and p-MLKL, which were reversed by pretreatment with SFN. Network pharmacology and molecular docking demonstrated that SFN could bind to TLR4 and inhibit NFκB pathway. The mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory factors IL6, CXCL16, iNOS and IL18 were down-regulated by SFN. SFN might alleviate LPS-induced macrophage PANoptosis through TLR4/NFκB pathway, thereby inhibiting macrophage inflammation and becoming a potential therapeutic drug for sepsis-induced ALI.
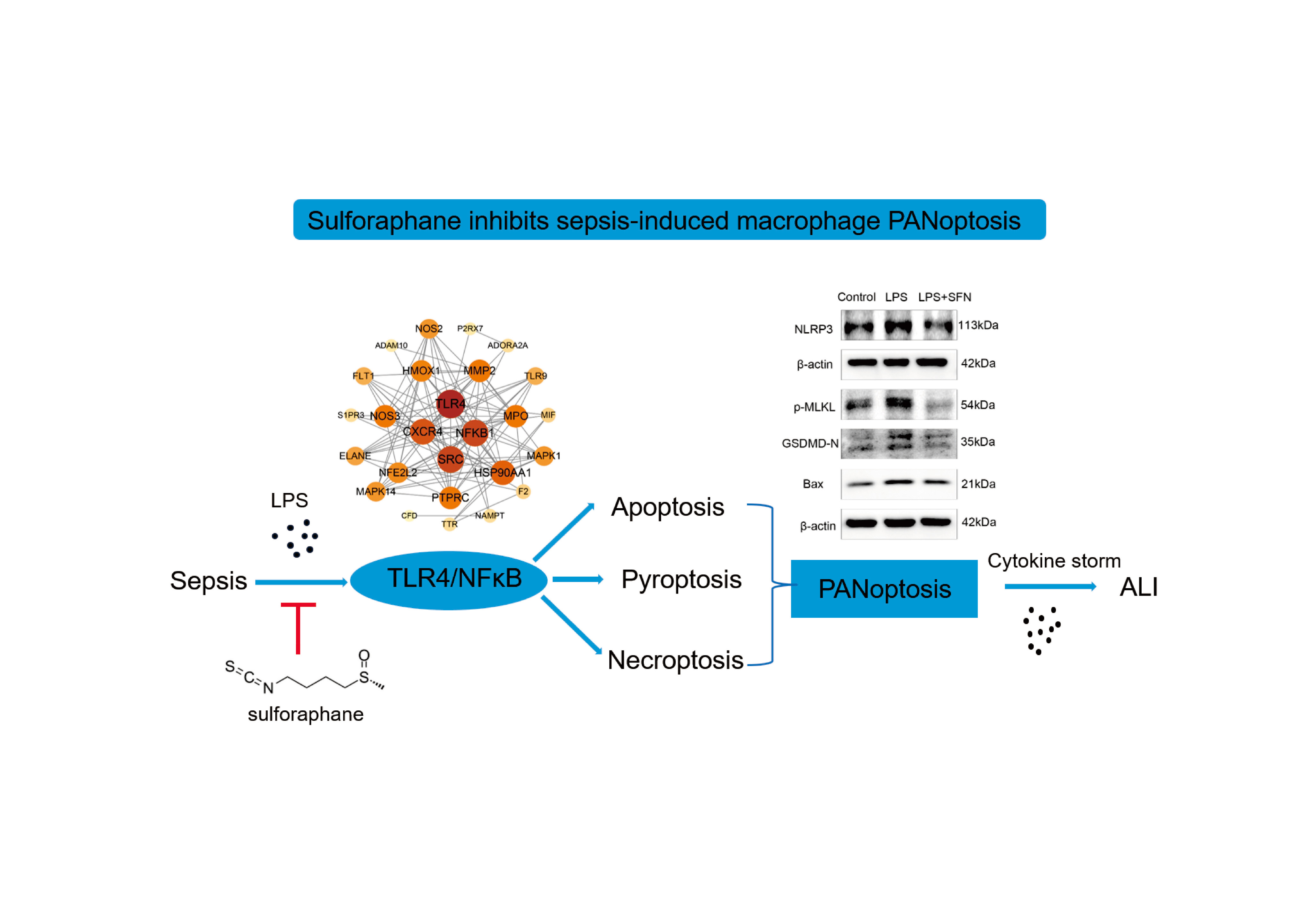 View full abstractDownload PDF (3190K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3190K) Full view HTML
-
Xue Zheng, Taowu Gong, Wanqiu Yu, Shan Xu, Chunchun Tang, Yuanping Zho ...Article type: Review
2025Volume 265Issue 4 Pages 249-259
Published: 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 02, 2025
Advance online publication: November 28, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLNeuroinflammation is a major pathological mechanism of neurodegenerative disease-triggered cognitive disorders. Currently, no preventative measures or therapies are available. Gastrodin (GAS), an effective monomer derived from Gastrodia, is considered to be an anti-inflammatory candidate to attenuate microglia-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. The present study first modelled the inflammatory activation of BV2 cells, which was induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) at the molecular level. The optimal concentration of GAS was screened out to preliminarily investigate its role in improving the inflammatory activation of BV2 cells during cellular death. Then, the research further discussed how GAS ameliorated inflammation via regulating ferroptosis. According to the results of our study, GAS up-regulates downstream heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) expression while lowers reactive oxygen species (ROS) expression by Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) nuclear transposition. Experimental results showed that 100 µM is the optimal concentration for gastrodin in the inflammatory activation model. GAS can promote Nrf2 nuclear translocation and the expression of HO-1 and NQO1 while reduce ROS level. Therefore, GAS can regulate ferroptosis in LPS-induced BV2 cellular inflammation model, thus attenuating inflammatory occurrence. In conclusions, GAS is considered to be an anti-inflammatory candidate that acts in LPS-induced BV2 cellular inflammation model by regulating ferroptosis.
View full abstractDownload PDF (2823K) Full view HTML
-
Toshiro Niki, Haorile Chagan-Yasutan, Daisuke Furushima, Toshio Hattor ...Article type: Regular Contribution
2025Volume 265Issue 4 Pages 261-269
Published: 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 02, 2025
Advance online publication: November 07, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDamage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) are endogenous molecules released from damaged tissues and elicit strong inflammatory responses of the host. Hence, they are supposed to play essential roles in the disrupted immune homeostasis after traumatic injuries. We examined plasma levels of galectin-9 (Gal-9), an immune checkpoint molecule as well as a DAMP, and a representative DAMP, high-mobility group box-1 (HMGB-1) in the trauma patient. Gal-9 was very high at admission, declined swiftly, and reached the normal level in 48 hours, while HMGB-1 was highest at admission, declined in 24 hours, then stagnated through the assessment period of 7 days with a level much higher than that of healthy subjects. The concentration of these DAMPs at admission correlated well with each other. HMGB-1 correlated with 6 prognostic parameters compared to only 2 for Gal-9, which reflects HMGB-1 but not Gal-9 could discriminate between survived and deceased patients. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis demonstrated that plasma HMGB-1 possesses a moderate prognostic potential to discriminate deceased patients from survivors. Collectively, HMGB-1 has a potential to make a valuable blood biomarker for trauma, possibly in combination with other blood biomarkers.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (791K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (791K) Full view HTML -
Guanjun Wu, Lei Gao, Xin Zhang, Qi Xue, Lifang Ye, Yaru Zheng, Jianlei ...Article type: Regular Contribution
2025Volume 265Issue 4 Pages 271-278
Published: 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 03, 2025
Advance online publication: November 07, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAngiogenesis is regarded as a critical factor in the pathogenesis of unstable atherosclerotic plaques, and numerous proteins and microRNAs (miRNAs) were involved in this process. In our previous study, the overexpression of Chitinase 3-like 1 (CHI3L1) aggravates the neo-vessels in carotid plaques of apoE-/- mice fed with a high-fat diet. MiR-24-3p is one of target miRNAs adjusting the expression of CHI3L1. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway is an important regulator related to cell proliferation and pathophysiological process of CHI3L1. This study aims to investigate whether the miR-24-3p plays a role in migration and proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) through influencing the expression of CHI3L1 and potential molecular mechanism. CCK8 assay, transwell and matrigel tests were used to determine the effects of miR-24-3p on proliferation, migration and tube formation of HUVECs by targeting CHI3L1. Luciferase assay was carried out to value the direct interaction between miR-24-3p and CHI3L1 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR). Western blot was used to measure protein expression of CHI3L1, ERK and phosphorylation of ERK (p-ERK). This study demonstrated that miR-24-3p mimic inhibits the proliferation, migration and angiogenesis of HUVECs. The role of miR-24-3p affects the function of HUVECs through negative regulation of CHI3L1 expression targeting CHI3L1 3′-UTR. Furthermore, we found that p-ERK was accordant with CHI3L1 expression in HUVECs, and miR-24-3p mimics significantly diminished the CHI3L1 expression and the level of p-ERK. MiR-24-3p is one of miRNAs regulating the expression and function of CHI3L1, which may provide an efficient strategy for treatment of angiogenesis in atherosclerotic plaques.
View full abstractDownload PDF (4594K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|