
- Issue 4 Pages 221-
- Issue 3 Pages 143-
- Issue 2 Pages 51-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Ayako Ide-Okochi, Mu He, Yumie Kanamori, Tomonori Samiso, Kayoko Takam ...2024Volume 262Issue 3 Pages 143-155
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 07, 2024
Advance online publication: January 18, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMental health deterioration after a disaster is a concern. Individuals’ sociability is expected to relate to the risk of this deterioration; however, research focusing on older adults is lacking. We aimed to investigate the relationship between psychological distress and sociability in older adults who survived the 2016 Kumamoto earthquake. We conducted a self-reported questionnaire survey in 2020. Data on 3,588 people aged 65 years and over (2,024 women and 1,564 men, mean age 74.6 ± 7.2, mean ± standard deviation) were analyzed. The overall prevalence of psychological distress (the Kessler psychological distress scale: K6 ≧ 10) was 10.5%; by gender, it was 11.2% in women and 9.5% in men. Logistic regression analysis revealed that, in the total sample, age, gender, public housing, reduction in income resulting from the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic, self-rated unhealthy conditions, subjective social isolation, and a lack of awareness of community events were positively associated with psychological distress. For women, a lack of community participation was positively related to psychological distress. For men, not knowing the change in school district after relocation was negatively associated with psychological distress, probably due to men’s scarce community participation and reliance on friendships, compared to women’s stronger dependence on community. Moreover, having a family member or friend to consult with was associated with a lower risk of psychological distress, regardless of gender. Gender differences were related to different conditions of social participation and types of social relationships. Enhancing community participation and family relationships among women and social contact with friends among men is essential.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (475K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (475K) Full view HTML -
Guangwen Long, Qian Zhang, Xiulin Yang, Hongpeng Sun, Chunling Ji2024Volume 262Issue 3 Pages 157-162
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 12, 2024
Advance online publication: November 09, 2023JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLPulmonary fibrosis (PF) is the major complication and death-related factor of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). This study evaluated the significance of miR-141-3p in ARDS and its complication of PF aiming to identify a potential biomarker for screening ARDS and predicting the occurrence of PF. A total of 137 ARDS patients and 69 healthy individuals were enrolled in this study and the serum samples were collected from all participants. The serum miR-141-3p levels were analyzed by polymerase chain reaction. The significance of miR-141-3p in the diagnosis and development of ARDS, and the occurrence of PF was evaluated by receiver operating curve, Chi-square test, and logistic regression analysis. MiR-141-3p was downregulated in ARDS patients and showed significant potential in its diagnosis. Reduced miR-141-3p was significantly associated with the increasing Murray and APACHEII score and the occurrence of PF in ARDS patients. MiR-141-3p, Murray score, and APACHEII score were identified as risk factors for the occurrence of PF in ARDS, and miR-141-3p was also found to be downregulated in ARDS patients with PF. Additionally, miR-141-3p could discriminate ARDS patients with PF and without PF, and was closely associated with the decreased total lung capacity, carbon monoxide diffusing capacity, and forced vital capacity of ARDS patients with PF. Downregulated miR-141-3p served as a biomarker for ARDS screening disease onset and indicating the severity. Reduced miR-141-3p was also identified as a risk factor for PF in ARDS patients and was associated with the severe progression of PF.
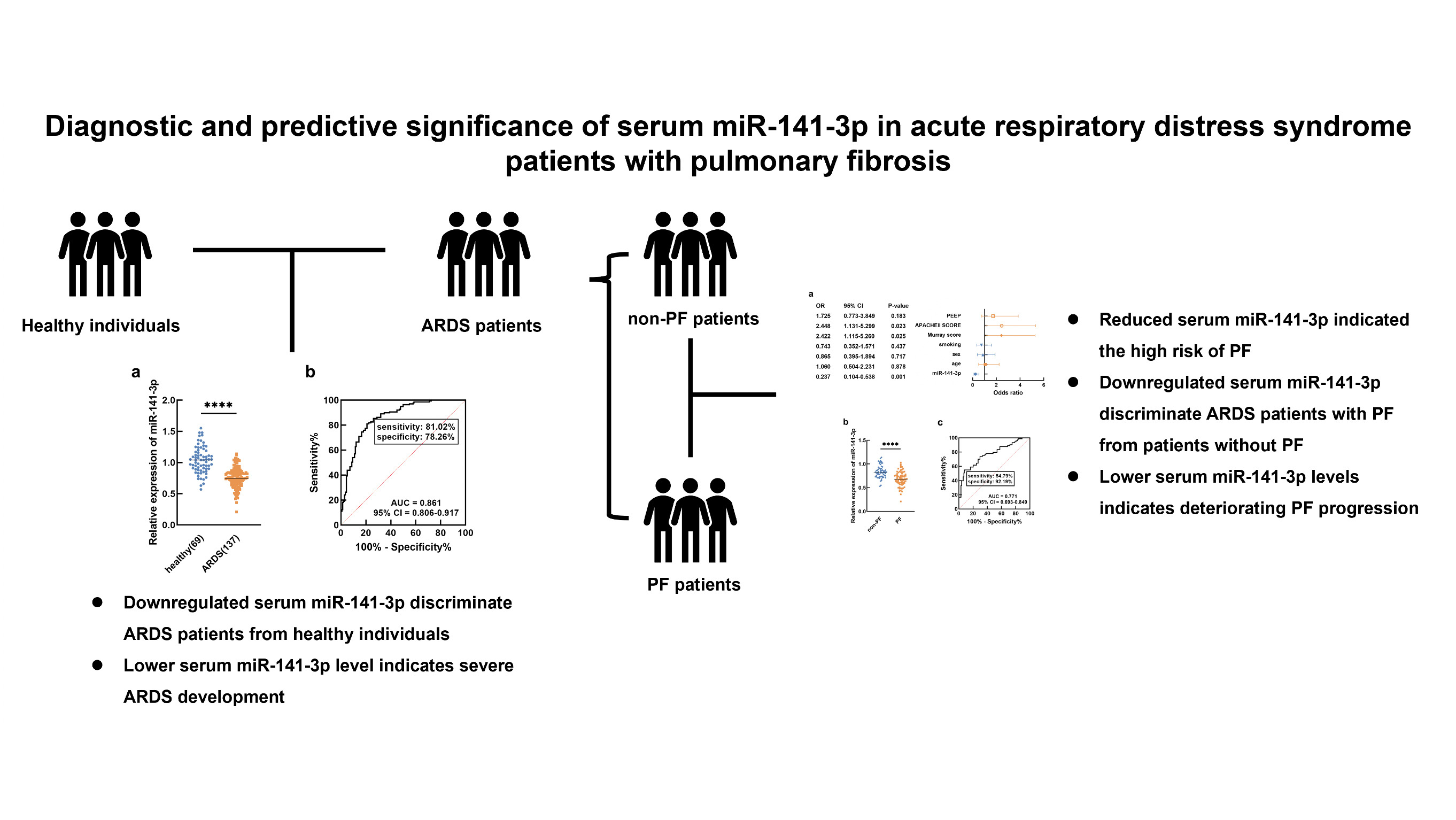 View full abstractDownload PDF (567K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (567K) Full view HTML -
Yasuhiro Suzuki, Yasufumi Sato2024Volume 262Issue 3 Pages 163-171
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 12, 2024
Advance online publication: January 12, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAs pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is extremely malignant and refractory, therapeutic options for this cancer are anticipated worldwide. We isolated vasohihibin-2 (VASH2) and observed its overexpression in various types of cancer. We then noticed that upregulated expression of VASH2 in patients with PDAC resulted in a conspicuous reduction in the postoperative survival period and further revealed that the abrogation of Vash2 expression in pancreatic cancer cells inhibited its growth and metastasis and augmented tumor infiltration of CD8+ cells in the mouse model. We developed VASH2-targeting therapies, 2′,4′-BNA-based antisense oligonucleotide targeting VASH2 (VASH2-ASO) as a nucleotide-based therapy, and VASH2-peptide vaccine as an antibody-based therapy. We also showed that the VASH2-peptide vaccine inhibited PDAC metastasis in an orthotopic mouse model. Here, we expanded our analysis of the efficacy of VASH2-targeting therapies for PDAC. VASH2-ASO treatment inhibited the growth of primary tumors by reducing tumor angiogenesis, normalizing tumor vessels, preventing ascites accumulation and distant metastasis to the liver and lungs, and augmenting the infiltration of CD8+ cells in metastatic tumors. VASH2-peptide vaccine did not affect the infiltration of CD8+ cells into tumors. The present study revealed that VASH2-targeting therapies are promising options for the treatment of PDAC. VASH2-ASO therapy can be administered at any stage of PDAC. Because of the increase of CD8+ cell infiltration, the combination therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors may be an attractive option. The VASH2-peptide vaccine therapy may be useful for preventing metastasis and/or recurrence after successful initial treatment.
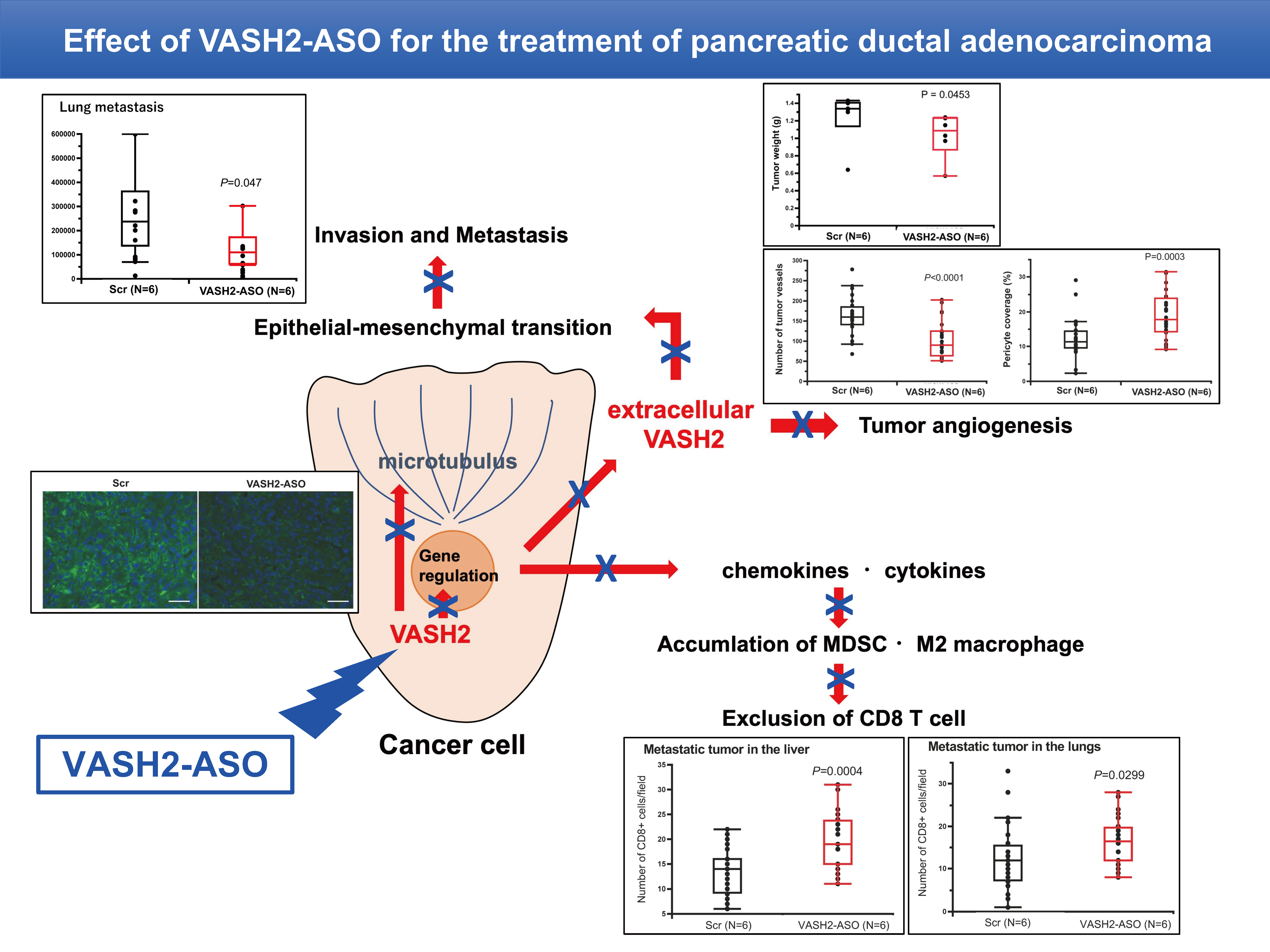 View full abstractDownload PDF (4991K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (4991K) Full view HTML -
Liqiao Chen, Liangliang Wang, Zongqi Han, Peng Qin, Guangxu Niu, Jingx ...2024Volume 262Issue 3 Pages 173-180
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 15, 2024
Advance online publication: December 21, 2023JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLSKI-349 is a novel sphingosine kinases (SPHK) inhibitor with anti-tumor effects. This study aimed to assess the effect of SKI-349 on cell biological behaviors, downstream pathways, and its synergistic effect with sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HCC cell lines (Huh7 and Hep3B) were treated with SKI-349 at concentrations of 1, 2, 4, or 8 μM. Then, SPHK1/2 activity, cell viability, proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and protein expressions of phosphorylated-protein kinase B (p-AKT), AKT, phosphorylated-mammalian target of rapamycin (p-mTOR) and mTOR were detected. Combination index values of SKI-349 (0, 1, 2, 4, or 8 μM) and sorafenib (0, 2.5, 5, 10, or 20 μM) were calculated. SKI-349 decreased the relative SPHK1 and SPHK2 activity compared with blank control in a dose-dependent manner in the Huh7 and Hep3B cell lines. Meanwhile, SKI-349 reduced cell viability, 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) positive cells, and invasive cells, while it increased apoptotic cells compared to blank control in a dose-dependent manner in Huh7 and Hep3B cell lines. Based on the western blot assay, SKI-349 decreased the ratio of p-AKT to AKT and that of p-mTOR to mTOR compared with blank control in a dose-dependent manner in the Huh7 and Hep3B cell lines. Additionally, SKI-349 combined with sorafenib declined cell viability with concentration gradient effects compared to SKI-349 sole treatment, and they had synergistic cytotoxic effects in Huh7 and Hep3B cell lines. SKI-349 suppresses SPHK1 and SPHK2 activity, cell viability, invasion, and AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, as well as exhibits a synergistic cytotoxic effect with sorafenib in HCC.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (5138K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (5138K) Full view HTML -
Kedong Han, Zhijiang He, Yunjun Liu, Hua Chen2024Volume 262Issue 3 Pages 181-189
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 15, 2024
Advance online publication: December 21, 2023JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLSome studies have investigated the role of cholesterol in the progression of colorectal cancer (CRC). However, the underlying mechanism of action is not clear. In this study, we used bioinformatics tools to elucidate the molecular mechanisms involved. We initially obtained CRC datasets from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and hypercholesterolemia data from GeneCards and DisGeNE. Common differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were determined by using Venn diagram web tools. Next, we performed Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses using the Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID). The hub gene was identified through common expression pattern analysis and survival analysis. Finally, we conducted an immune regulatory point analysis and predicted target drugs based on the hub gene. The results of our analysis revealed 13 common DEGs, with endothelin receptor type A (EDNRA) identified as the hub gene linking hypercholesterolemia and CRC. The results of the GO analysis showed that the common DEGs were primarily associated with the G-protein coupled receptor signaling pathway, extracellular space, and receptor binding. The results of the KEGG pathway enrichment analysis indicated enrichment in pathways related to cancer and the phospholipase D signaling pathway. Additionally, we identified potential target drugs, including Podocarpus montanus, Diospyros kaki, Herba Salviae japoniae, sitaxentan, and ambrisentan. We found that EDNRA might be an underlying biomarker for both hypercholesterolemia and CRC. The predicted target drugs provide new strategies for treating CRC.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2853K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2853K) Full view HTML -
Bo-Wen Yin, Liu Yang2024Volume 262Issue 3 Pages 191-199
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 16, 2024
Advance online publication: December 28, 2023JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTreatment-resistant depression (TRD) poses significant therapeutic challenges despite available interventions. Escitalopram (ESC) is a highly selective antidepressant. This study aimed to compare ESC alone and ESC combined with modified electroconvulsive therapy (MECT) or high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (HF-rTMS) in TRD patients. Ninety participants were randomized into ESC alone, ESC + MECT, and ESC + HF-rTMS groups. Notable differences were observed in Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS-17) scores at 12 weeks among ESC (14.37), ESC + MECT (10.27), and ESC + HF-rTMS (10.77) groups (P = 0.006). In terms of overall quality of life (QoL) evaluated using the World Health Organization Quality of Life Questionnaire (WHOQOL-BREF) at 12 weeks, the ESC, ESC + MECT, and ESC + HF-rTMS groups scored 2, 3, and 3.5, respectively. ESC + MECT/HF-rTMS groups showed reduced depressive symptoms compared to the ESC group, accompanied by higher overall QoL scores and increased satisfaction with health. Patients receiving ESC + MECT demonstrated no significant alterations in short-term memory and orientation, as measured by the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), before and after treatment. Moreover, a decline in language was observed compared to baseline (12 weeks: median 2, IQR 2-3; baseline: median 1, IQR 1-3; P = 0.022). The positive impact of ESC with HF-rTMS on cognitive function was evidenced by improvements in all domines MoCA.Combining ESC with MECT or HF-rTMS exhibited enhanced effectiveness in alleviating depressive symptoms and enhancing QoL compared to ESC monotherapy. Specifically, the ESC + HF-rTMS combination displayed potential as a comprehensive treatment strategy for TRD, addressing both emotional and cognitive aspects.
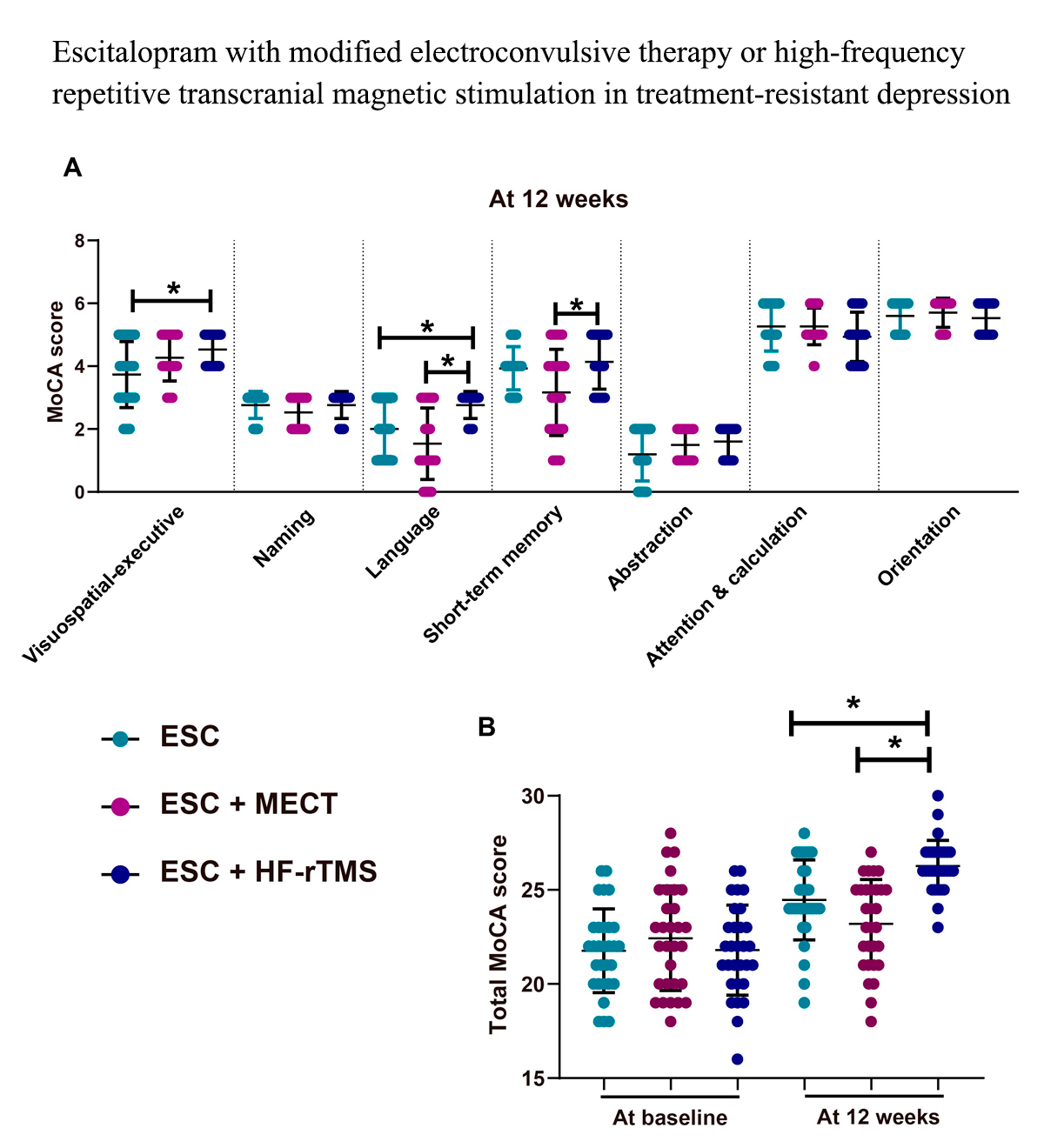 View full abstractDownload PDF (1461K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1461K) Full view HTML -
Hui Yin2024Volume 262Issue 3 Pages 201-209
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 16, 2024
Advance online publication: December 28, 2023JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThis study aimed to assess the impact of enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) intervention in preventing venous thromboembolism (VTE) among postoperative lung cancer patients. Conducted from January 2022 to January 2023, the research involved 125 lung cancer patients randomly assigned to either a control group (n = 60) receiving routine care, or an ERAS group (n = 65) which received both routine care and ERAS interventions. The ERAS program comprised a comprehensive series of interventions meticulously implemented throughout the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative phases. Thrombotic risk assessment using the Caprini Risk Assessment Model (RAM) was conducted preoperatively and on postoperative day 5 (POD 5), with plasma D-dimer levels measured preoperatively, on POD 1, POD 3, and POD 5. Quality of life and patient satisfaction were assessed at discharge using the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Quality of Life Questionnaire-Lung Cancer Module 13 (QLQ-LC13) and The Newcastle Satisfaction with Nursing Scale (NSNS), respectively. The ERAS group demonstrated significantly lower Caprini RAM scores on POD 5 compared to the control group, with lower D-dimer levels on POD 3 and POD 5. The incidence of VTE was lower in the ERAS group (1.54%) compared to the control group (11.67%) during hospitalization. At discharge, the ERAS group showed improved quality of life, with higher satisfaction scores for nursing care and their hospital stay. ERAS nursing interventions effectively mitigate thrombotic risk, improve D-dimer levels, enhance postoperative quality of life, and elevate patient satisfaction among individuals undergoing lung cancer surgery.
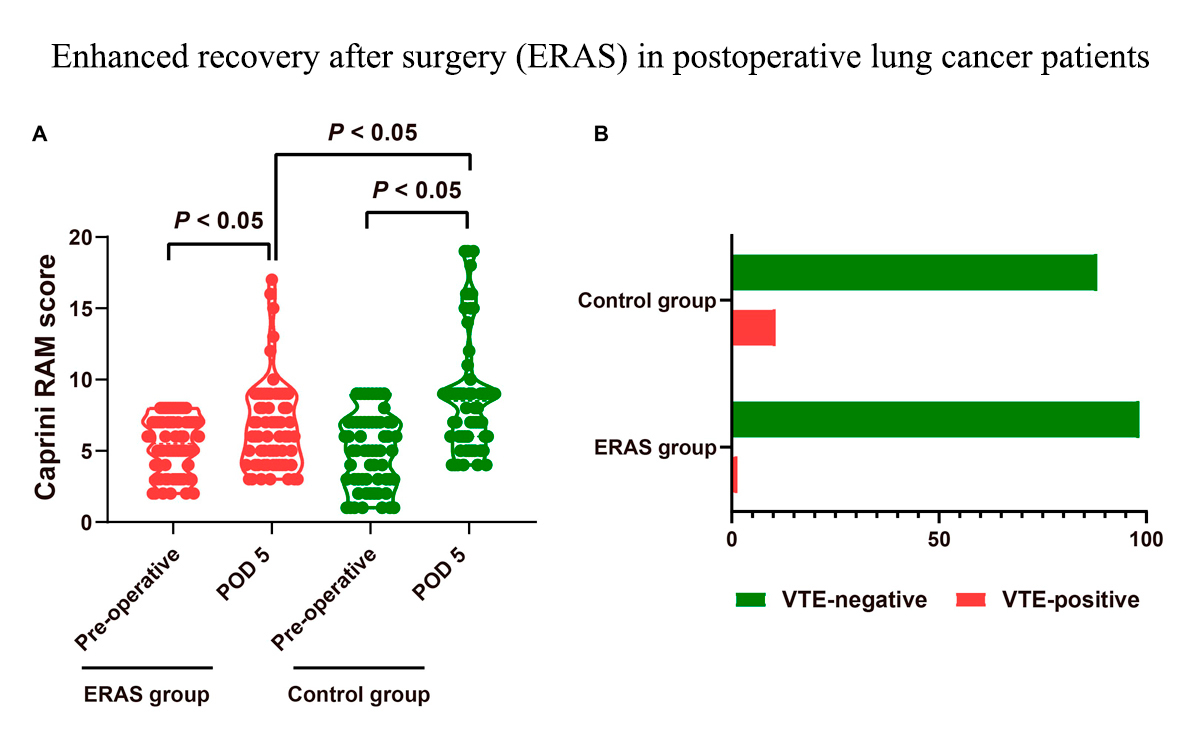 View full abstractDownload PDF (997K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (997K) Full view HTML -
Kuan-Hung Liu, Teng-Lung Kuo, Nai-Ying Ko, Yi-Heng Li, Wen-Chien Ko, S ...2024Volume 262Issue 3 Pages 211-220
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 19, 2024
Advance online publication: December 28, 2023JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
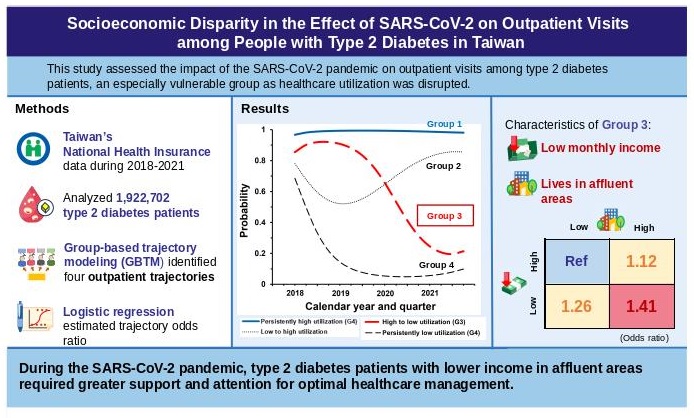
Supplementary materialThe severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) outbreak posed impact on healthcare. This study evaluated the effect of SARS-CoV-2 outbreak on the outpatient visits of patients with type 2 diabetes and determined the most affected groups. We analyzed Taiwan’s National Health Insurance data, including 1,922,702 patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes from 2018 to 2021. Group-based trajectory modelling identified four distinct outpatient visit patterns, namely, consistently high (Group 1, 74.2%), low-to-high (Group 2, 8.1%), high-to-low (Group 3, 6.0%) and consistently low (Group 4, 11.7%) utilization. Logistic regression was used to analyze correlations between trajectory types and patients’ demographics and health statuses. Group 3 members had higher odds of being male [adjusted odds ratio (aOR) = 1.04, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.03-1.05] and earning below 20,000 New Taiwan Dollar monthly (aOR = 1.29, 95% CI 1.26-1.31) than those in Group 1. However, they were less likely to be under 80 years old (aOR = 0.70-0.97), from lower median family income regions (aOR = 0.81-0.89) or possess a Charlson Comorbidity Index score > 2 (aOR = 0.67, 95% CI 0.66-0.68). Patients with lower income in affluent areas displayed the highest likelihood of falling into Group 3. Patients with type 2 diabetes and low income from wealthy areas were vulnerable during the pandemic. This result emphasizes the need to target resources and support for this subgroup during such crises.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (451K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (451K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|